Innovative water-based dynamic liquid bubble membrane generation device for gas/vapour separation
Carbon dioxide represents the largest contribution among the emitted greenhouse gases. Therefore, avoiding the use of traditional fossil fuels such as coal and oil is highly desirable. Both natural gas and biogas produced from renewable raw materials contain methane as the active component are environmentally more friendly energy sources. However, these gases typically contain a significant percentage of carbon dioxide on top of minor amounts of other gases, which reduces the energy utilization of the gas. Therefore, new economically and environmentally beneficial technologies are being sought in addition to well-established technologies, including adsorption, amine treatment, and water washing. Considerable efforts are currently focused on the design, development, and application of membrane processes for gas separation because membranes are relatively simple, less energy intensive, and easily scalable. The current weakness of most membranes is the well-known “trade-off” between permeability and selectivity, i.e. the membrane is typically not both highly selective and highly permeable.
The group of Dr. Uchytil has been dealing with the topic of gas and vapor separation using membranes of various types for a long time. One of the directions is the use of liquid membranes for the separation of carbon dioxide from gaseous mixtures. The work recently published in the Chemical Engineering Journal follows several years of research into a unique type of membrane system called dynamic liquid membranes characterized by high selectivity and gas permeability and low cost. The work describes equipment for the separation of gas mixtures using a dynamic liquid bubble membrane (DLBM), which has demonstrated excellent separation efficiency for CO2/CH4 and CO2/O2 systems in laboratory conditions. The principle of DLBM is a continuously regenerated network of bubbles filled with a mixture of gases; the gases are separated on the thin liquid film of the bubble walls due to the different solubilities of the gases in the liquid forming the bubbles. The idea of the DLBM system is novel in membrane technology; the advantages are the few microns thick liquid film providing high flux, the unique construction of the experimental device ensuring the continuous regeneration of the liquid film during the process, and the tailored composition of the liquid film for high membrane selectivity.
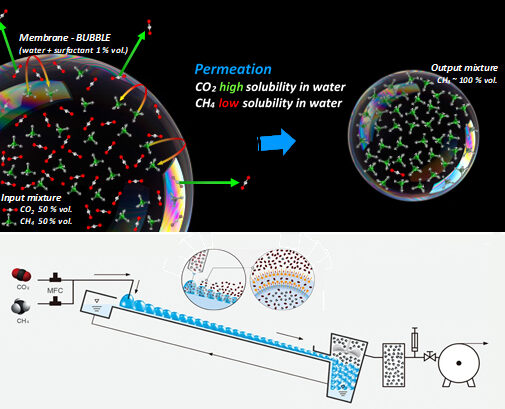
Schematic of the separation mechanism of the bubble membranes and the DLBM apparatus designed for gas/vapour mixture separation
- Lin, Y.C.; Setničková, K.; Wang, D.K.; Chu, Y.F.; Šíma, V.; Chiang, Y.Y.; Uchytil, P.; Tseng, H.H.: Innovative water-based dynamic liquid bubble membrane generation device for gas/vapour separation. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 450(3), 138233-138242. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2022.138233