Rheology of hydrogels and their nanocomposites
Hydrogels and their nanocomposites are materials that are widely used today, from the pharmaceutical sector (contact lenses, wound dressings, drug delivery) to the environmental sector (effective adsorbents). Although these materials have been used for several decades, their preparation is typically focused only on the ratio of reactants in the reaction mixture, regardless of the amount of water present. As part of our research, we tested the targeted control of the water content of polyacrylamide hydrogels by varying the water content during polymerization. At the same time, the morphology and strength of the hydrogel are related to the water content, so these properties can be adjusted as needed.
The influence of the structure and composition of hydrogel nanocomposites on their properties (morphology, rigidity and especially their selectivity and adsorption capacity for organic dyes) was also studied. The type of additive (graphene, k
aolin or laponite), its content and the water content in the polyacrylamide hydrogel nanocomposite were varied. It was found that the most effective way to increase the adsorption capacity for organic dyes is the addition of laponite, selectively for cationic dyes having phenyl groups in their structure. Adsorption isotherms showed that nanocomposites with medium water content (i.e. optimal pore size) were the most effective adsorbents.
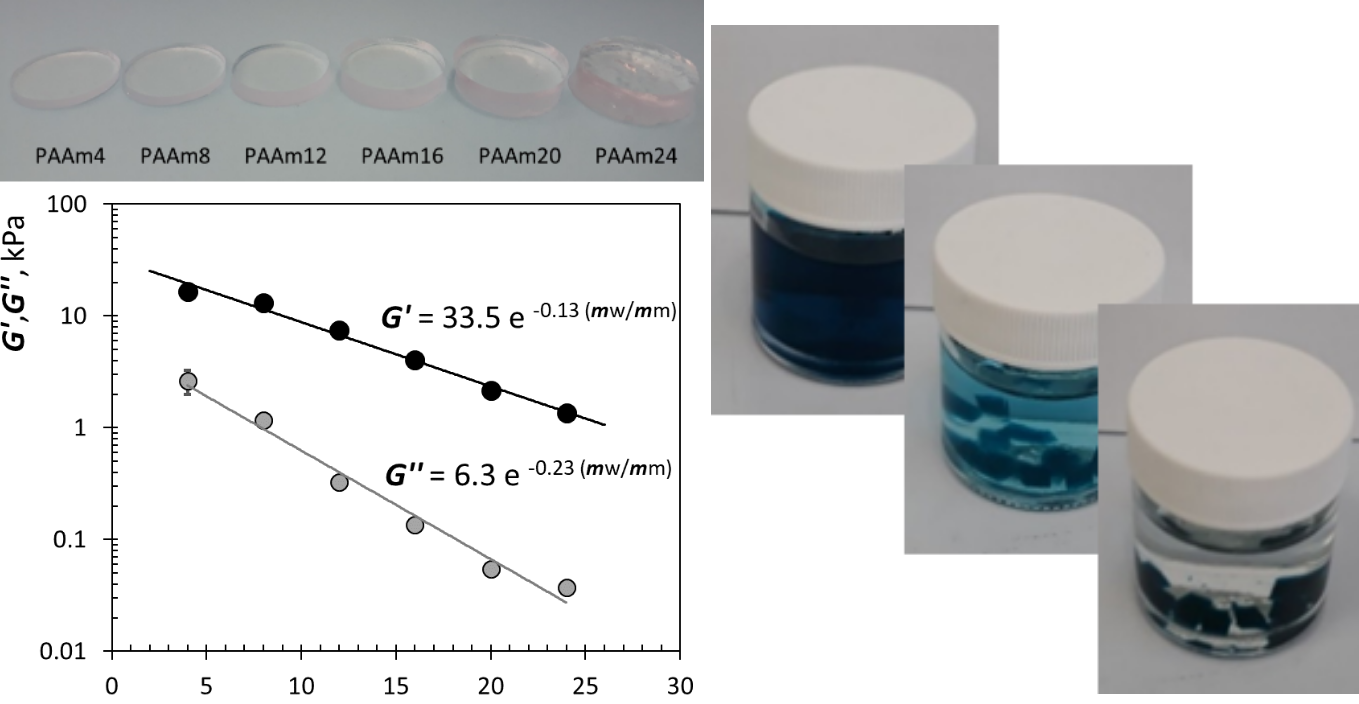
Fig. The volume of the hydrogel increases with increasing water content, while the rigidity in terms of elastic and viscous moduli decreases (left). Time course of adsorption of brilliant green onto laponite nanocomposite (right).
Penkavova, A. Spalova, J. Tomas, J. Tihon, Polyacrylamide hydrogels prepared by varying water content during polymerization: Material characterization, reswelling ability, and aging resistance, Polymer Engineering & Science 62 (2022) 901-916. DOI: 10.1002/pen.25895
Penkavova, A. Spalova, J. Tihon, Polyacrylamide hydrogel-based nanocomposites containing graphene, kaolin or laponite: Physico-mechanical characterization and adsorption properties, Materials Today Communications 34 (2023) 105150. DOI: 10.1016/j. mtcomm.2022.105150