Technical catalysis for socially responsible production
 catalysts based on polymeric nanofibre supports prepared by electrospinning for reactions in the gas and liquid phase (pollutant elimination, synthesis of fine chemicals)
catalysts based on polymeric nanofibre supports prepared by electrospinning for reactions in the gas and liquid phase (pollutant elimination, synthesis of fine chemicals)- supported catalysts for hydrorefining of fuels, Guerbet reaction, and catalytic decomposition of hydrogen sulfide
Physico-chemical processes for environmental protection
- catalysts for the total oxidation of volatile organic compounds
- advanced physicochemical methods for the removal of pollutants from water
- hierarchically structured sorbents for contaminant removal
- photocatalysts for pollutant removal from water
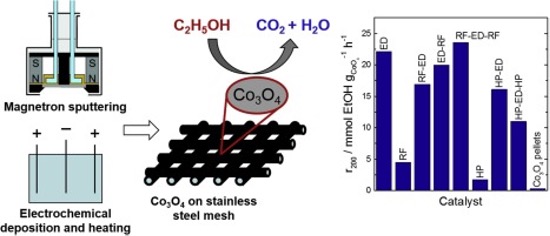
The activity of catalysts prepared by magnetron sputtering and electrochemical deposition in ethanol oxidation
Characterization of microstructural properties of porous materials with complicated (hierarchical) porosity
 advanced textural analysis of porous materials using state-of-the-art computational approaches based on density functional theory (DFT, NLDFT, QSDFT)
advanced textural analysis of porous materials using state-of-the-art computational approaches based on density functional theory (DFT, NLDFT, QSDFT)- determination of effective transport properties of porous materials in gas and liquid phases
- measurement of high-pressure adsorption isotherms on materials suitable for gas storage (H2, CO2, CH4)
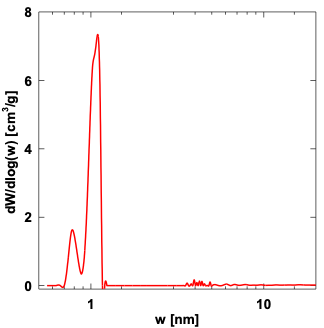
Pore size distribution by Ar physisorption at 87K
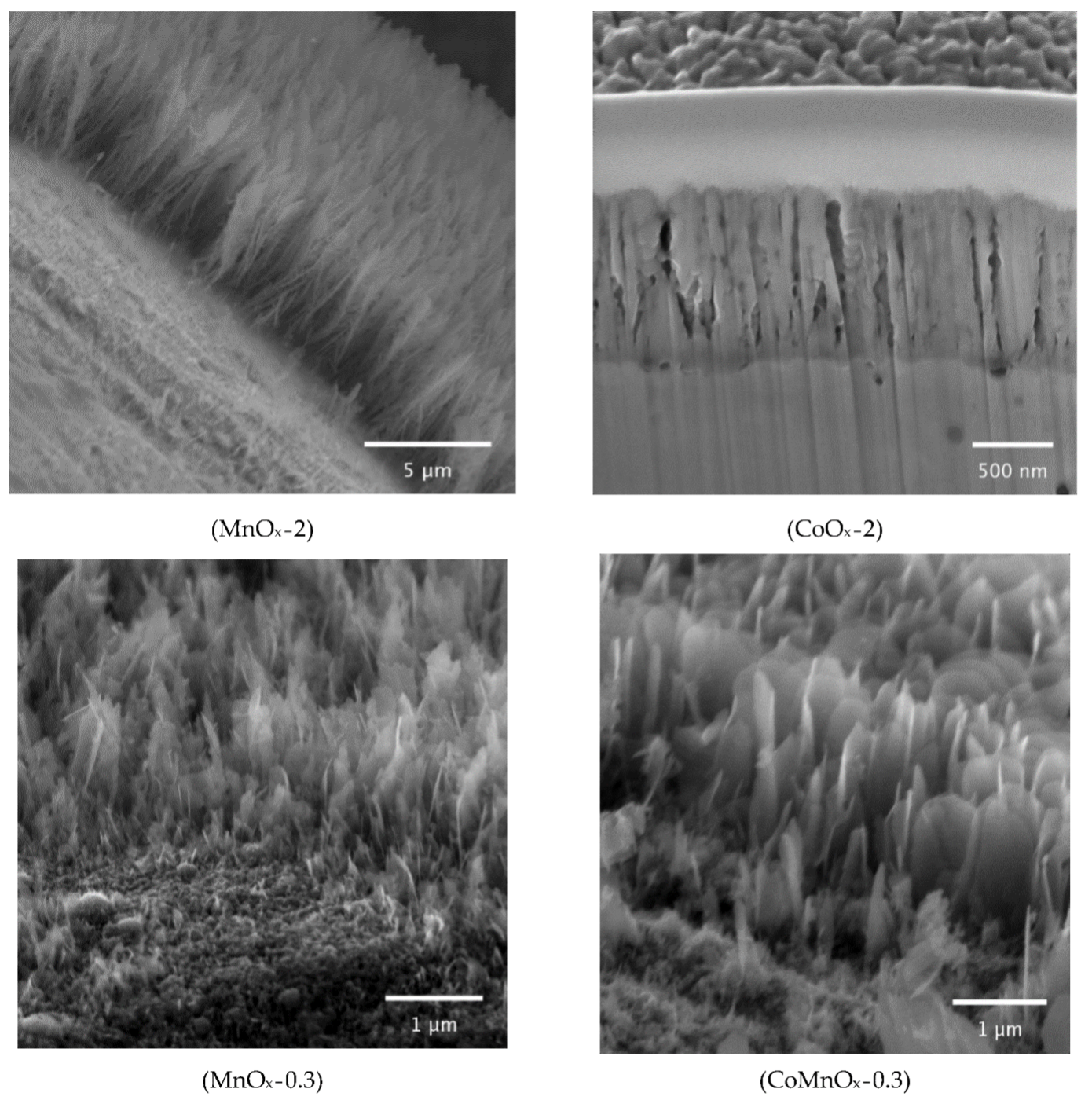
Effect of manganese addition to Ni-Cu oxides on their properties and activity in the oxidation of volatile organic compounds
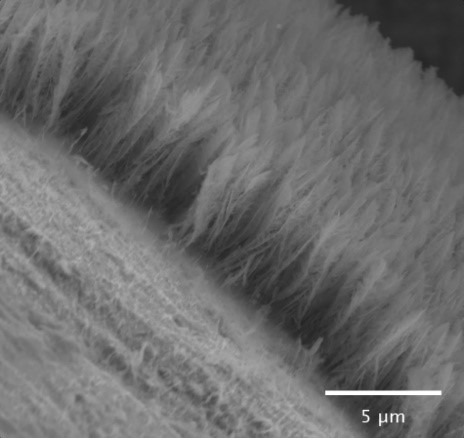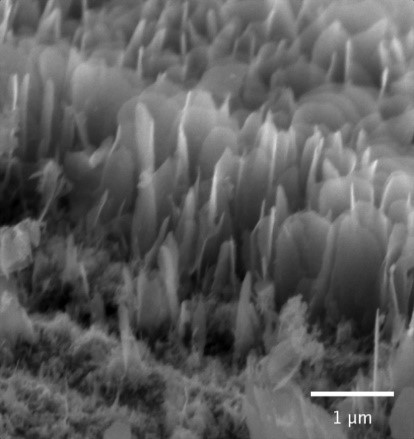
 Transition metal oxides are suitable for the reduction of harmful volatile organic compounds in air by total catalytic oxidation. The effect of Mn addition to Ni-Cu oxides was investigated to determine the optimum cation composition for achieving high catalytic performance. The addition of Mn to Ni-Cu oxides led to the formation of Ni-Cu-Mn mixed oxides with spinel structure and Ni-Mn mixed oxides. As the Mn concentration increased, the concentration of metal-bound oxygen raised, while the concentration of oxygen vacancies slightly decreased. A linear correlation was revealed between the surface concentrations of oxygen vacancies and specific reaction rates in ethanol and toluene oxidation.
Transition metal oxides are suitable for the reduction of harmful volatile organic compounds in air by total catalytic oxidation. The effect of Mn addition to Ni-Cu oxides was investigated to determine the optimum cation composition for achieving high catalytic performance. The addition of Mn to Ni-Cu oxides led to the formation of Ni-Cu-Mn mixed oxides with spinel structure and Ni-Mn mixed oxides. As the Mn concentration increased, the concentration of metal-bound oxygen raised, while the concentration of oxygen vacancies slightly decreased. A linear correlation was revealed between the surface concentrations of oxygen vacancies and specific reaction rates in ethanol and toluene oxidation.
- Jirátová K., Babii T., Balabánová J., Koštejn M., Maixner J., Topka P., Kovanda F.: Effect of manganese addition to Ni-Cu oxides on properties and activity in the oxidation of volatile organic compounds. Catal. Today 429(1 Mar), 114463, 2024. DOI
Dioxins and furans in biochars, hydrochars and torreficates produced by thermochemical conversion of biomass
 Converting raw biomass into valuable products protects the environment, improves economics, and helps tackle climate change by cutting resource demand and waste production. Thermochemical treatment is a common method for producing biochars, hydrochars, and torreficates from biomass and organic wastes, which can also generate dioxins and furans and consequently limit the use of thermochemically converted chars. Here we review the presence of dioxins and furans in chars produced by hydrothermal carbonization, torrefaction, and pyrolysis processes under the influence of temperature, residence time, heating rate, pressure, and feedstock type. Dioxins and furans were mostly below 20 ng total toxic equivalence per kilogram (TEQ kg-1) with the highest level of 113 ng TEQ kg-1 found in over 100 samples of different char types.
Converting raw biomass into valuable products protects the environment, improves economics, and helps tackle climate change by cutting resource demand and waste production. Thermochemical treatment is a common method for producing biochars, hydrochars, and torreficates from biomass and organic wastes, which can also generate dioxins and furans and consequently limit the use of thermochemically converted chars. Here we review the presence of dioxins and furans in chars produced by hydrothermal carbonization, torrefaction, and pyrolysis processes under the influence of temperature, residence time, heating rate, pressure, and feedstock type. Dioxins and furans were mostly below 20 ng total toxic equivalence per kilogram (TEQ kg-1) with the highest level of 113 ng TEQ kg-1 found in over 100 samples of different char types.
- Sobol L., Dyjakon A., Soukup K.: Dioxins and furans in biochars, hydrochars and torreficates produced by thermochemical conversion of biomass: a review. Environ. Chem. Lett. 21, 2225-2249, 2023. DOI
The effect of lithium on NiMo/Al2O3 hydrotreating catalysts prepared from heteropolycompounds
Recently, simultaneous hydrotreatment of various petroleum fractions and plant feedstocks has been in demand. Nickel-molybdenum catalysts can be active in these processes. Therefore, NiMo oxide catalysts have been prepared by impregnating an alumina support with Anderson molybdenum salt and lithium carbonate. The prepared catalysts were tested in the hydrodesulfurization (HDS) of thiophene and the parallel hydrodeoxygenation (HDO) of 1-benzothiophene and octanoic acid. Experimental data showed a positive effect of lithium on the parallel HDS/HDO reactions and a negative effect on the HDS of thiophene. A significant effect of lithium on the acidity and reducibility of the NiMo/Al2O3 catalyst as well as the contribution of an Anderson-type heteropolymer compound was demonstrated.
- Kaluža L., Jirátová K., Spojakina A.A., Balabánová J., Gulková D., Koštejn M., Palcheva R., Tyuliev G., Fajgar R.: The Effect of Lithium on NiMo/Al2O3 Hydrotreating Catalysts Prepared from Heteropolycompounds. Catal. Lett. 154, 430-447, 2024. DOI
Novel catalytic materials based on polymer nanofiber supports
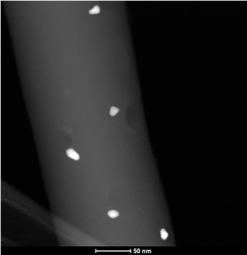 Low pressure drop across the catalytic bed due to high porosity (< 80%) and the presence of macropores in the nanofibrous support
Low pressure drop across the catalytic bed due to high porosity (< 80%) and the presence of macropores in the nanofibrous support- High availability of catalytically active components (negligible effect of internal diffusion)
Hydrorefining catalysts
- Supported (Al2O3, TiO2, or ZrO2) sulfide catalysts based on Co, Mo, and Ni for hydrotreating fuels
- New catalysts with optimized microstructure for hydrotreating liquefiable wastes derived from plastics and heavy oil fractions
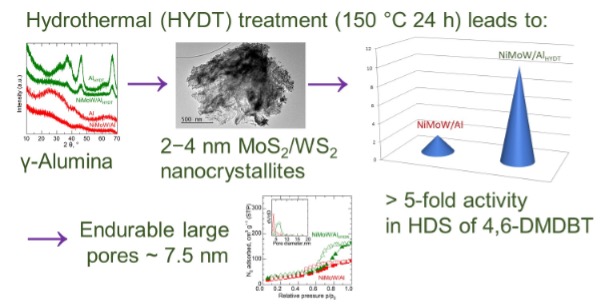 Effect of hydrothermal treatment on the hydrodesulfurization activity of sulfided nickel-molybdenum-wolfram catalysts
Effect of hydrothermal treatment on the hydrodesulfurization activity of sulfided nickel-molybdenum-wolfram catalysts
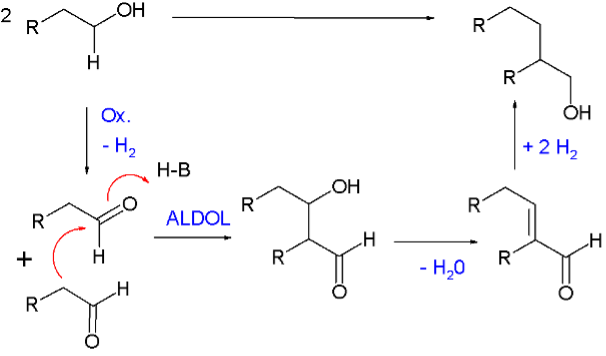
Guerbet reaction catalysts
- High surface area catalysts based on MgO, Ni/MgO, and Co/MgO
- Catalysts with optimized microstructure for Guerbet condensation of primary alcohols (bioethanol and biobutanol) to form a mixture of liquid fuels (alkanes, alkenes) and higher alcohols with emphasis on high selectivity
Catalysts for hydrogen sulphide decomposition
- MoS2-based supported catalysts for the direct decomposition of sulfate to hydrogen and elemental sulfur without the formation of CO2
- Recovery of refinery waste gases containing H2S (replacement of the Claus process)
Comparison of the hydrodesulfurization activity of catalysts prepared by conventional impregnation and a newly developed water-assisted spreading method
Catalysts for the complete oxidation of volatile organic compounds
- Structured catalysts based on transition metal oxides deposited on stainless steel meshes by plasma methods
- Low-pressure drop across the catalytic bed, high activity compared to commercial catalysts
Sorbents and photocatalysts for the removal of pollutants from water
- Carbon sorbents and photocatalysts for the removal of contaminants from water (pharmaceuticals, pesticides, or endocrine disruptors)
- Sorption capacity of sorbents prepared from renewable sources (biomass) comparable to commercial sorbents
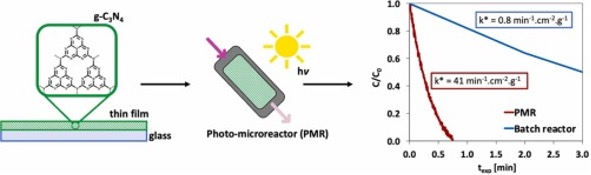 Comparison of conversion in a photo-microreactor and a packed bed reactor in the photodegradation of pollutants
Comparison of conversion in a photo-microreactor and a packed bed reactor in the photodegradation of pollutants