CuSix cathode for electrochemical CO2 reduction
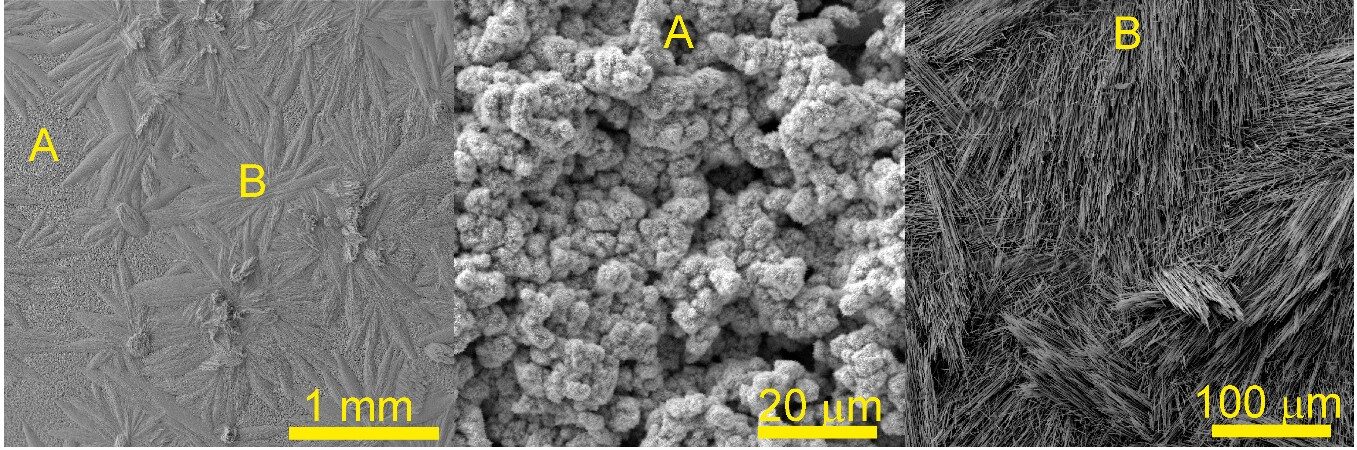 The CVD deposition method was used to prepare a copper silicide cathode CuxSi (3<x<5). Butylsilane BuSiH3 was passed in a quartz tube over a Cu substrate, thermally decomposed at 550 °C and 300-400 Pa pressure, forming a porous copper silicide structure and nanostructures with predominantly nano- and micro-rods on the surface. Two different versions of the catalyst grew at different precursor flow rates – one had a SiCx layer grown on it, while the other did not. Both variants retained catalytic activity without significant reduction even after 720 h of electrochemical measurements. The CuxSi catalyst showed high selectivity towards ethanol (~79%) in neutral CO2-saturated electrolyte and acetic acid (~72%) in alkaline medium.
The CVD deposition method was used to prepare a copper silicide cathode CuxSi (3<x<5). Butylsilane BuSiH3 was passed in a quartz tube over a Cu substrate, thermally decomposed at 550 °C and 300-400 Pa pressure, forming a porous copper silicide structure and nanostructures with predominantly nano- and micro-rods on the surface. Two different versions of the catalyst grew at different precursor flow rates – one had a SiCx layer grown on it, while the other did not. Both variants retained catalytic activity without significant reduction even after 720 h of electrochemical measurements. The CuxSi catalyst showed high selectivity towards ethanol (~79%) in neutral CO2-saturated electrolyte and acetic acid (~72%) in alkaline medium.
- Dřínek V., Dytrych P., Fajgar R., Klementová M., Kupčík J., Kopeček J., Svora P., Koštejn M., Jandová V., Soukup K., Beranek R.: A robust and high performance copper silicide catalyst for electrochemical CO2 reduction. Materials Advances, 2024. DOI