Photochemistry
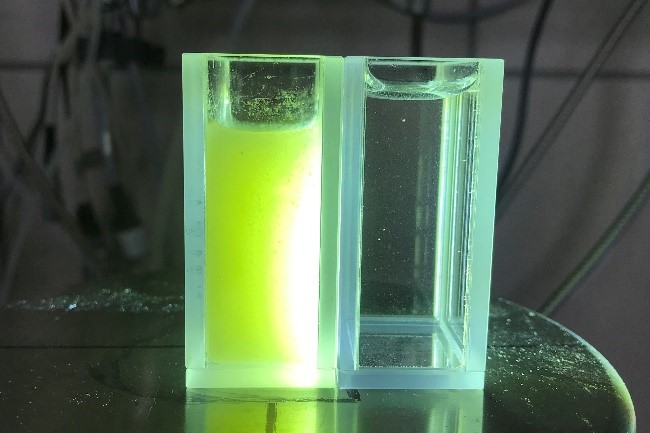
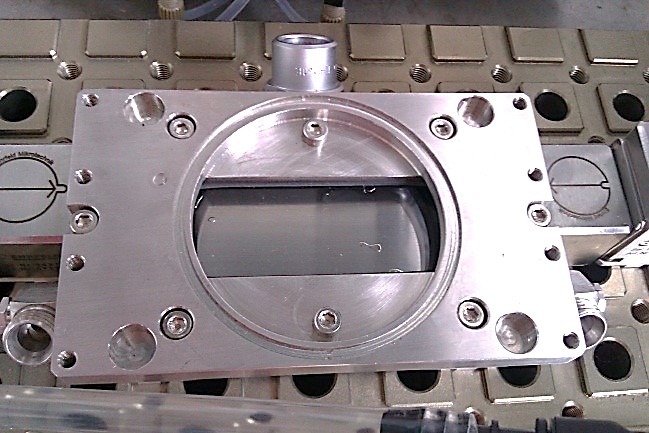
We focus on the development, testing, and characterization of highly functional thin films on the basis of graphitic carbon nitride (g-C3N4) for visible light-induced pollutant degradation and water splitting. The goal is to obtain highly active and durable photocatalytic films with application-tailored properties such as thickness, porosity, and photocatalytic activity. The cost-effective and reproducible method synthesis for highly active g-C3N4 is investigated. The photo activity of the prepared films is tested with a unique photo-microreactor of a slit geometry on an optical bench.
 |
 |
Batch-to-continous transformations
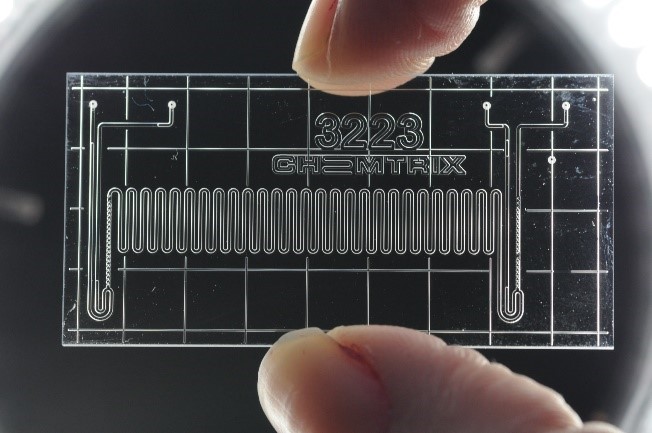
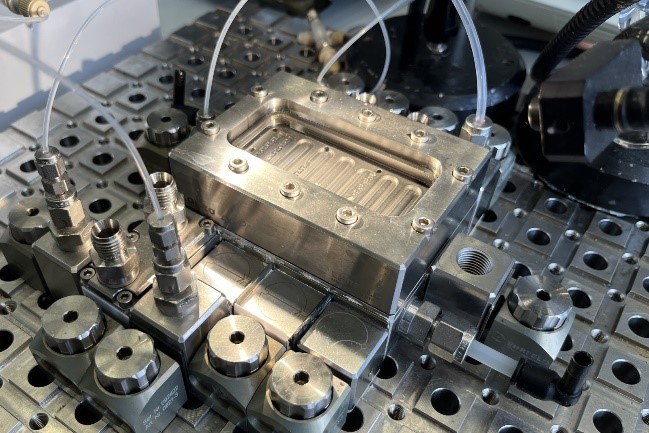
Batch-to-continuous transformation of phase-transfer catalyzed N-alkylation reactions for the synthesis of pharmaceuticals. This case study of N-alkylation of lysergic acid derivatives represents a fast, exothermic reaction occurring on the interface among aqueous and organic phases. Current state-of-the-art preparation includes batch process with yields of only about 80% and the use of toxic alkylation agents. Intensification of this mass-transfer limited reaction has the potential for yield increase as well as for toxic alkylation agent replacement by greener but less active alternative e.g. methyl carbonate.
 |
 |
3D printing in catalyst support and reactor design
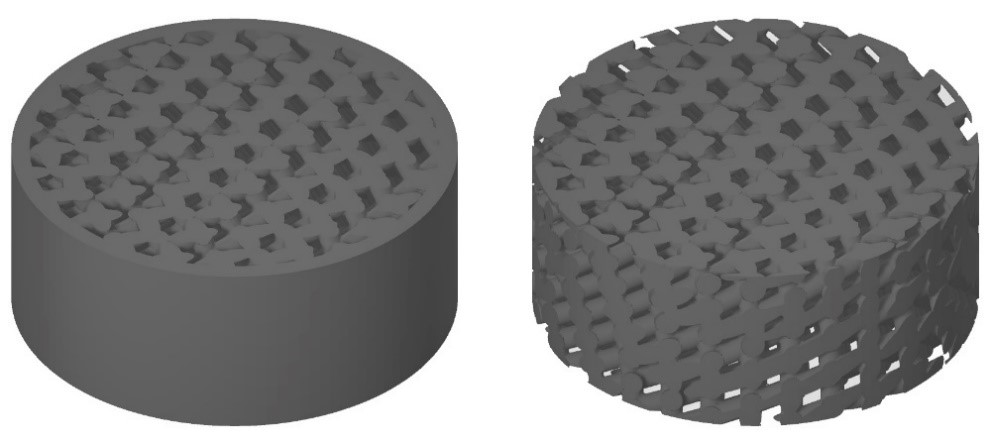 With the development of additive manufacturing technologies (3D printing), the Periodic Open Cellular Structures (POCS) are emerging as a suitable alternative to random particle beds, that represent the most utilized packed bed fillings for trickle bed catalytic reactors. POCS structures have a high potential for improving transport characteristics such as pressure drop, mass, and heat transport parameters by optimizing their geometry. The parametric set of POCS structures is designed, 3D printed, and experimentally examined for two-phase flow characteristics. The results will be compared with computational fluid mechanics (CFD) results to understand and describe the effect of geometry and topology on two-phase flow characteristics.
With the development of additive manufacturing technologies (3D printing), the Periodic Open Cellular Structures (POCS) are emerging as a suitable alternative to random particle beds, that represent the most utilized packed bed fillings for trickle bed catalytic reactors. POCS structures have a high potential for improving transport characteristics such as pressure drop, mass, and heat transport parameters by optimizing their geometry. The parametric set of POCS structures is designed, 3D printed, and experimentally examined for two-phase flow characteristics. The results will be compared with computational fluid mechanics (CFD) results to understand and describe the effect of geometry and topology on two-phase flow characteristics.
Phase transfer catalysis of N-alkylation of a lysergic acid derivative in microfluidic systems
 In the Research Group of Microreactors, we have developed a new method for preparing a compound derived from ergot, which is used in the production of nicergoline, a drug for the treatment of dementia and Alzheimer’s disease. The reaction takes place in a two-phase immiscible liquid system using phase transfer catalysis (PTC). Ultrasound was used to accelerate the process, improving mixing and mass transfer between the liquids. Four different flow reactor configurations were tested, including microchip and capillary systems, some of which were sonicated throughout their entire volume. The optimized method achieved high selectivity (95%) and a production rate of up to 23 g/h in a reactor with a volume of only 3 ml. It was also shown that the use of ultrasound can double the yield per unit volume of the reactor without compromising the efficiency of the reaction or the purity of the product. These results confirm that flow synthesis using microfluidic devices in combination with ultrasound can significantly improve the preparation of pharmaceutically important substances.
In the Research Group of Microreactors, we have developed a new method for preparing a compound derived from ergot, which is used in the production of nicergoline, a drug for the treatment of dementia and Alzheimer’s disease. The reaction takes place in a two-phase immiscible liquid system using phase transfer catalysis (PTC). Ultrasound was used to accelerate the process, improving mixing and mass transfer between the liquids. Four different flow reactor configurations were tested, including microchip and capillary systems, some of which were sonicated throughout their entire volume. The optimized method achieved high selectivity (95%) and a production rate of up to 23 g/h in a reactor with a volume of only 3 ml. It was also shown that the use of ultrasound can double the yield per unit volume of the reactor without compromising the efficiency of the reaction or the purity of the product. These results confirm that flow synthesis using microfluidic devices in combination with ultrasound can significantly improve the preparation of pharmaceutically important substances.
- Jaklova N., Stavarek P., Vychodilova H., Malikova S., Kluson P., Holas T.: Phase transfer catalysis of N-alkylation of a lysergic acid derivative in microfluidic systems. Eng. J. 2025, 523 (1 Nov) 167999. DOI
Light-sensitive coatings of graphitic carbon nitride with defined porosity
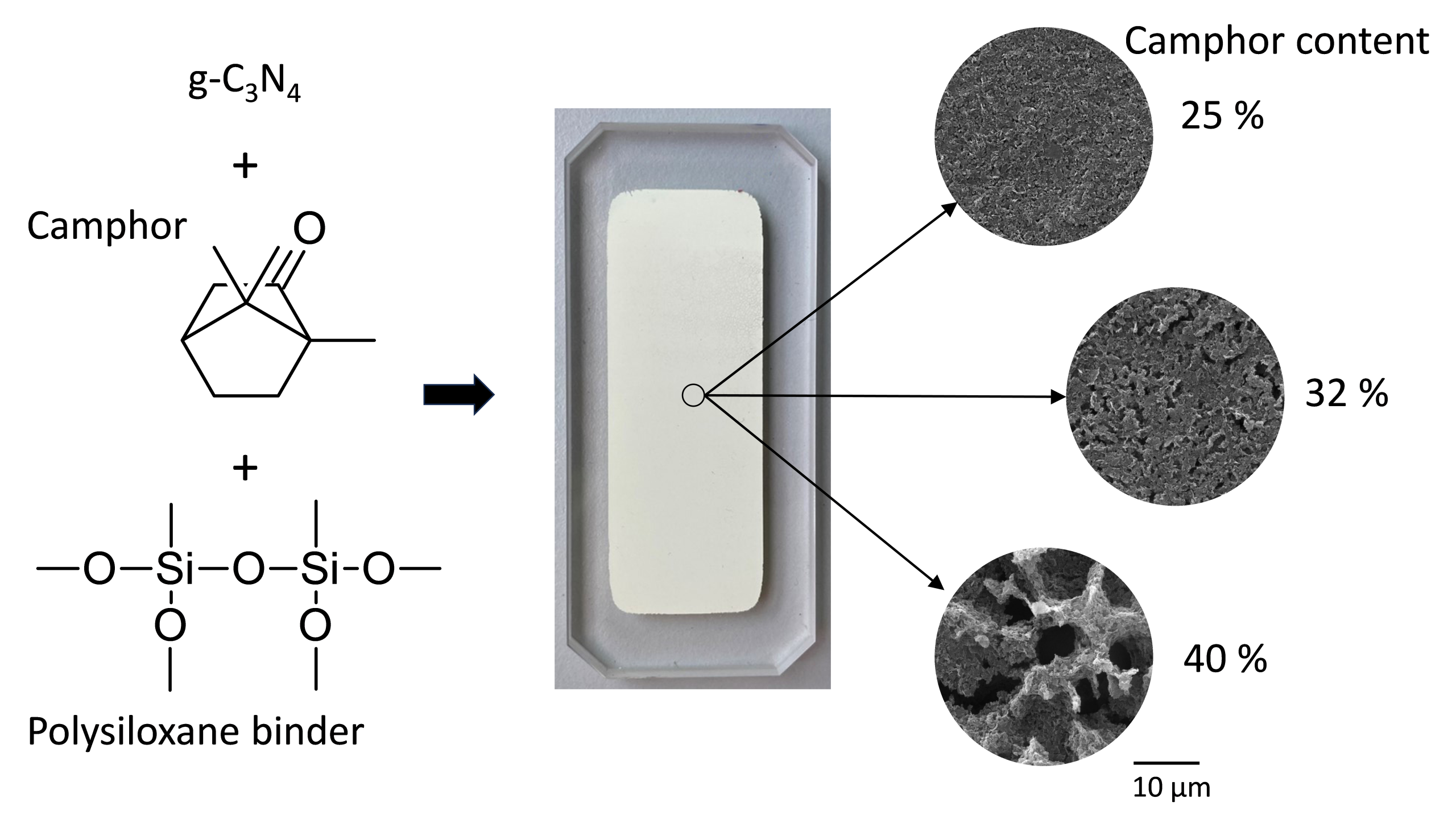 Graphitic carbon nitride (g-C3N4) is a light-sensitive material with strong potential in photocatalysis, though interpreting kinetic data in ox/redox reactions is often challenging. While fine porosity increases surface area, it is not always accessible to photons, leading to mass transport limitations instead of true kinetic control. This issue can be addressed by thin-film catalysts with surfaces directly exposed to light. Here, g-C3N4 thin films were prepared using porogenic camphor to tailor morphology and porosity, with further plasma treatment applied. Their structure and surface properties were extensively characterized. The films were tested for tetracycline oxidation in a slit-type micro-photoreactor and compared with coatings prepared without camphor and/or plasma treatment. The results show how surface engineering influences photocatalytic efficiency. Tetracycline degradation was chosen as a relevant model process due to its importance for wastewater decontamination containing pharmaceuticals.
Graphitic carbon nitride (g-C3N4) is a light-sensitive material with strong potential in photocatalysis, though interpreting kinetic data in ox/redox reactions is often challenging. While fine porosity increases surface area, it is not always accessible to photons, leading to mass transport limitations instead of true kinetic control. This issue can be addressed by thin-film catalysts with surfaces directly exposed to light. Here, g-C3N4 thin films were prepared using porogenic camphor to tailor morphology and porosity, with further plasma treatment applied. Their structure and surface properties were extensively characterized. The films were tested for tetracycline oxidation in a slit-type micro-photoreactor and compared with coatings prepared without camphor and/or plasma treatment. The results show how surface engineering influences photocatalytic efficiency. Tetracycline degradation was chosen as a relevant model process due to its importance for wastewater decontamination containing pharmaceuticals.
- Schimon D., Patakyová S., Stavárek P., Dzik P., Homola T., Zažímal F., Klusoň P.: Visible-light-sensitive coatings of graphitic carbon nitride with inherent porosity induced by camphor. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A-Chem. 2025, 468(1 Nov) 116507. DOI
Fatty nitrile esters for biosourced polyamide polymers
Po lyamides (e.g., nylon) are usually produced from amino acids, but a new alternative is amino esters, which can be obtained from renewable sources such as vegetable oils. These substances can be used to produce special high-value plastics such as Rilsan® (polyamide 11). However, production is not easy. When converting intermediates containing nitrile groups into amines (hydrogenation), it is necessary to achieve a very pure product so that the monomers are suitable for further processing. Therefore, we investigated how different catalysts, temperature, hydrogen pressure, or the addition of ammonia affect the course of the reaction and the resulting product quality. This work, in the form of a chapter in a book, not only summarizes the current state of knowledge in the field of nitrile hydrogenation, but also supplements it with our own experiments, calculations, and modeling in order to better understand the reaction mechanism and determine the optimal conditions for the preparation of amines from fatty acid nitrile esters for the industrial production of polyamides from renewable sources.
lyamides (e.g., nylon) are usually produced from amino acids, but a new alternative is amino esters, which can be obtained from renewable sources such as vegetable oils. These substances can be used to produce special high-value plastics such as Rilsan® (polyamide 11). However, production is not easy. When converting intermediates containing nitrile groups into amines (hydrogenation), it is necessary to achieve a very pure product so that the monomers are suitable for further processing. Therefore, we investigated how different catalysts, temperature, hydrogen pressure, or the addition of ammonia affect the course of the reaction and the resulting product quality. This work, in the form of a chapter in a book, not only summarizes the current state of knowledge in the field of nitrile hydrogenation, but also supplements it with our own experiments, calculations, and modeling in order to better understand the reaction mechanism and determine the optimal conditions for the preparation of amines from fatty acid nitrile esters for the industrial production of polyamides from renewable sources.
- Stavárek P., Lali F., Dubois J.-L.: 894 Fatty nitrile esters for biosourced polyamide polymers, in: K. Serge, D. Jean-Luc (Eds.), Industrial Green Chemistry 2nd Ed., De Gruyter 2025, pp. 89-128. DOI
Photocatalytic degradation of pharmaceuticals by visible light using thin films of graphitic carbon nitride
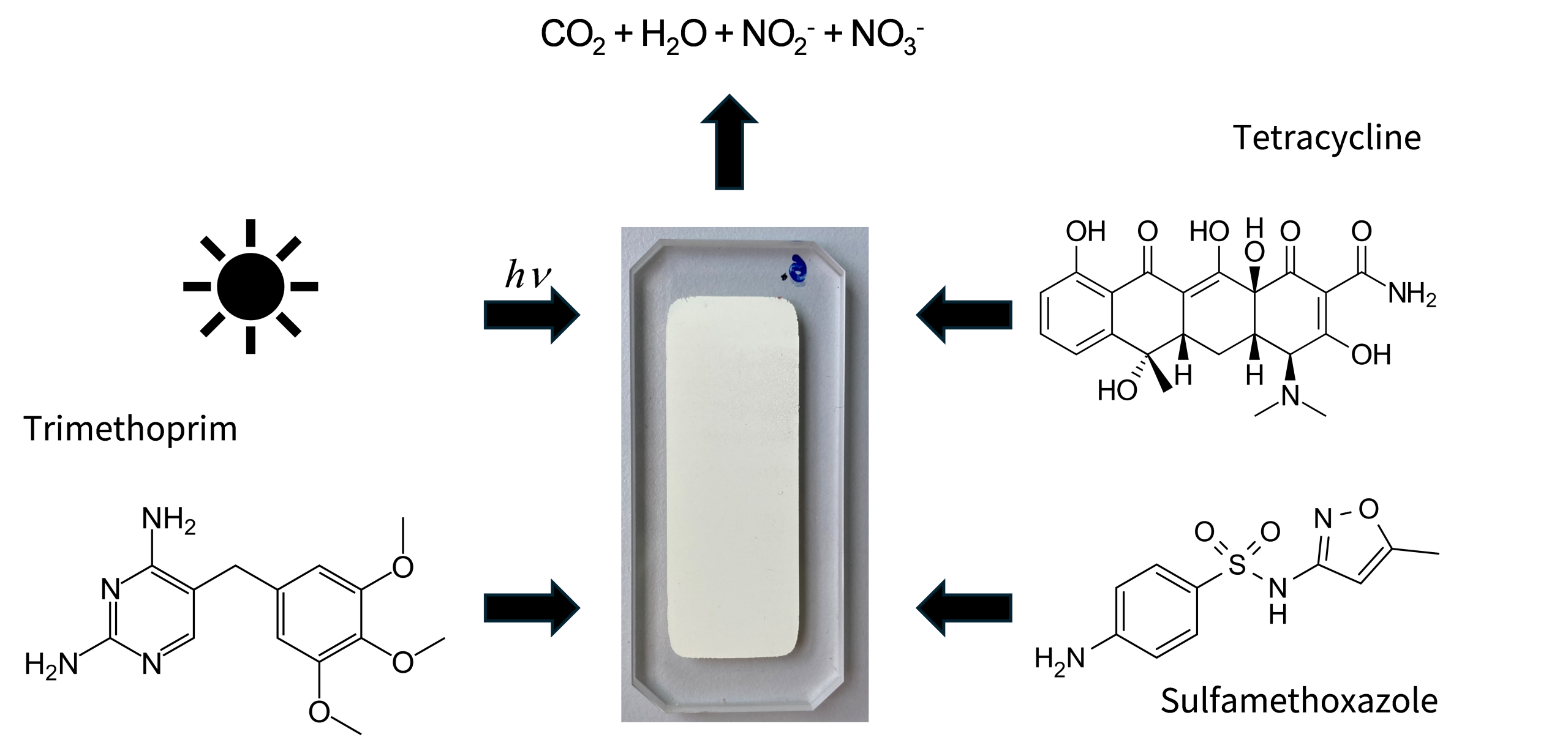 The release of pharmaceuticals and their metabolites into the environment poses pollution risks with consequences in fauna and flora that are not yet fully known nor understood. Photocatalytic degradation of these substances by graphitic carbon nitride (g-C3N4) using visible light could potentially contribute to reducing these risks. In this work, g-C3N4 was investigated in two different forms for the degradation of three selected antibiotics: tetracycline, trimethoprim, and sulfamethoxazole. Emphasis was placed on investigating the description of degradation pathways, modeling the mechanism, and comparing the two photoreactor systems. g-C3N4 in powder form was studied in a batch photoreactor, while g-C3N4 in the form of photocatalytic film was studied in a photomicroreactor with a slit geometry. It was found that during the photo-oxidation processes, the oxidation products of the starting material predominate in the reaction mixture, while degradation products of smaller molecular weight are directly mineralized. Comparison of the batch photoreactor and the microreactor with the developed photocatalytic film showed that the photomicroreactor was able to use the incident radiation more efficiently to degrade the investigated substances. This study was carried out in the framework of cooperation between the Research Group of Microreactors at the ICPF and the Faculty of Chemistry at Brno University of Technology and the Faculty of Science at Masaryk University in Brno.
The release of pharmaceuticals and their metabolites into the environment poses pollution risks with consequences in fauna and flora that are not yet fully known nor understood. Photocatalytic degradation of these substances by graphitic carbon nitride (g-C3N4) using visible light could potentially contribute to reducing these risks. In this work, g-C3N4 was investigated in two different forms for the degradation of three selected antibiotics: tetracycline, trimethoprim, and sulfamethoxazole. Emphasis was placed on investigating the description of degradation pathways, modeling the mechanism, and comparing the two photoreactor systems. g-C3N4 in powder form was studied in a batch photoreactor, while g-C3N4 in the form of photocatalytic film was studied in a photomicroreactor with a slit geometry. It was found that during the photo-oxidation processes, the oxidation products of the starting material predominate in the reaction mixture, while degradation products of smaller molecular weight are directly mineralized. Comparison of the batch photoreactor and the microreactor with the developed photocatalytic film showed that the photomicroreactor was able to use the incident radiation more efficiently to degrade the investigated substances. This study was carried out in the framework of cooperation between the Research Group of Microreactors at the ICPF and the Faculty of Chemistry at Brno University of Technology and the Faculty of Science at Masaryk University in Brno.
- Schimon D., Smítková K., Stavárek P.*, Jaklová N., Vanluchene A., Dzik P., Homola T., Zažímal F., Klusoň P.: A complex study of photocatalytic oxidation pathways of antibiotics with graphitic carbon nitride–The way towards continuous flow conditions. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2024, 12(6), 114801. DOI
Graphitic carbon nitride thin films for light-induced photocatalysis in a slit geometry microreactor
We have successfully prepared and tested thin films based on graphitic carbon nitride in a slit geometry microreactor. Films were prepared from the mixture of milled powder catalysts and a binder. The effects of post-annealing and plasma application were studied. The photoactivity was tested with the degradation of Rhodamine B and an antibiotic Tetracycline as an emerging pollutant in wastewater. The thin film form of the photocatalyst in the microreactor had about 50x higher specific activity compared to the slurry form.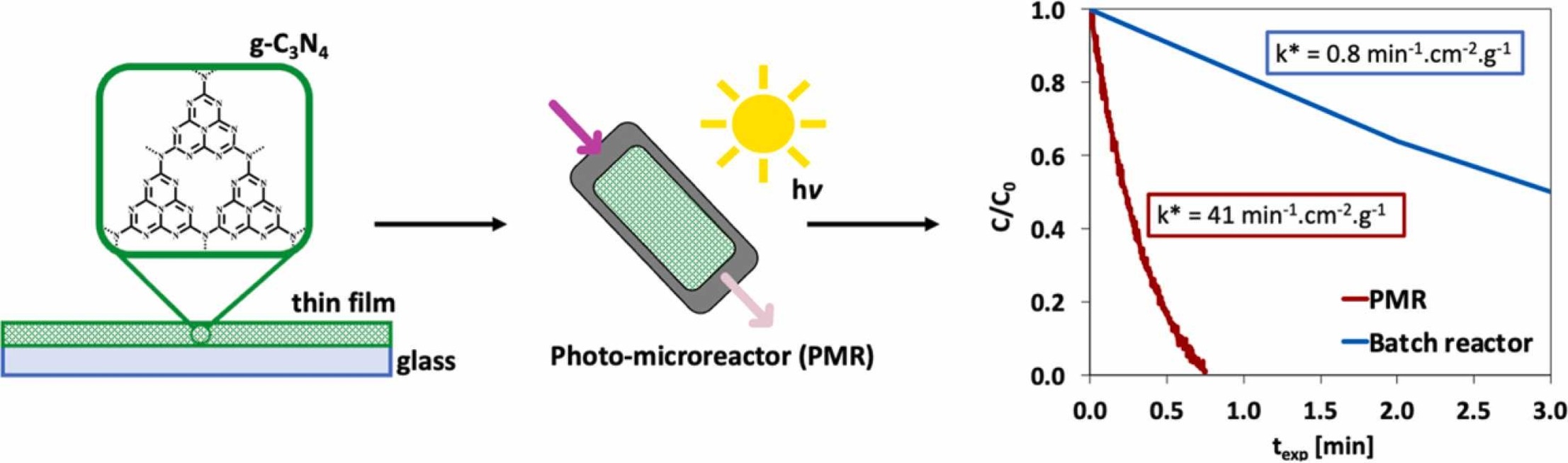
- Dolai S., Vanluchene A., Stavárek P., Dzik P., Fajgar R., Soukup K., Klusoň P., Graphitic carbon nitride thin films for light-induced photocatalysis in a slit geometry microreactor, J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 10(6), 108790, 2022. DOI
Design of the reversible biphasic arrangement in the microfluidic chip reactor for asymmetric hydrogenation reactions
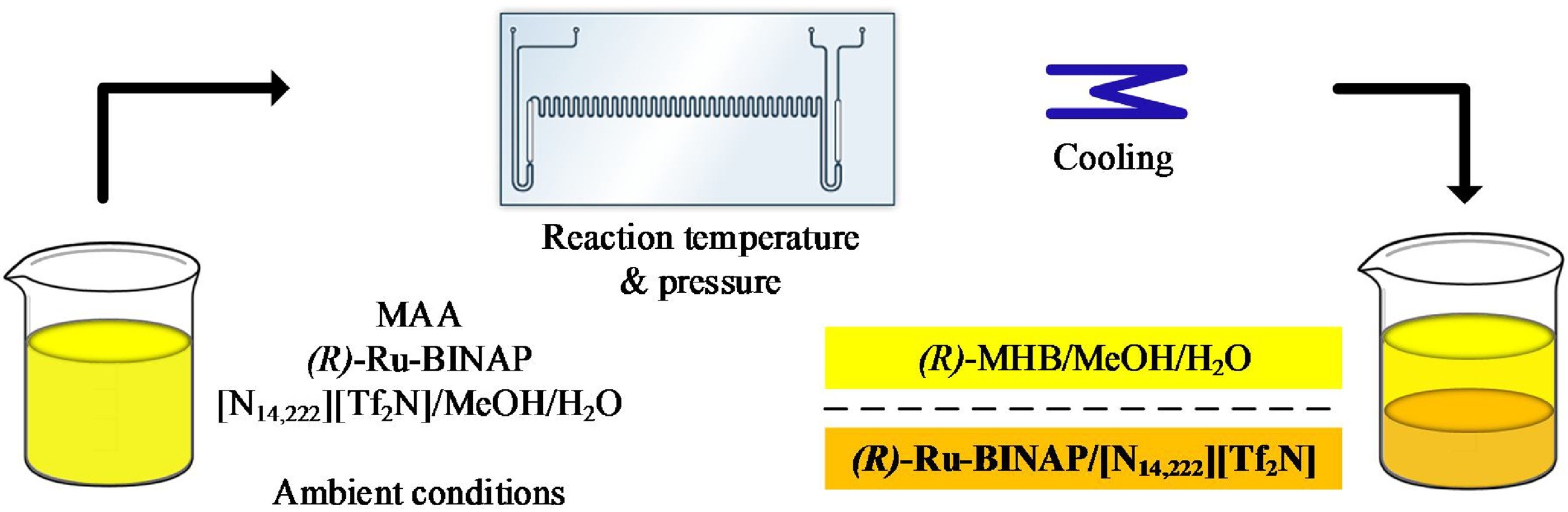 We have designed the reversible biphasic system for practical use in asymmetric hydrogenation performed in a microfluidic chip reactor. Methyl acetoacetate (MAA) was transformed to (R)-methyl hydroxybutyrate over optically pure (R)-Ru-BINAP catalyst as a model reaction. The reaction mixture is homogenous under reaction conditions while after the cooling two phases are formed. The methanolic phase contains the desired product, while the ionic liquid phase contains the ionic liquid with (R)-Ru-BINAP catalyst that can be simply reused in the reaction.
We have designed the reversible biphasic system for practical use in asymmetric hydrogenation performed in a microfluidic chip reactor. Methyl acetoacetate (MAA) was transformed to (R)-methyl hydroxybutyrate over optically pure (R)-Ru-BINAP catalyst as a model reaction. The reaction mixture is homogenous under reaction conditions while after the cooling two phases are formed. The methanolic phase contains the desired product, while the ionic liquid phase contains the ionic liquid with (R)-Ru-BINAP catalyst that can be simply reused in the reaction.
- Klusoň P., Stavárek P., Pěnkavová V., Vychodilová H., Hejda S., Bendová M., Došek M., Design of the reversible biphasic arrangement in the microfluidic chip reactor for asymmetric hydrogenation reactions. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 153, 537-546, 2020. DOI
Microreactor for gas-solid catalytic reactions
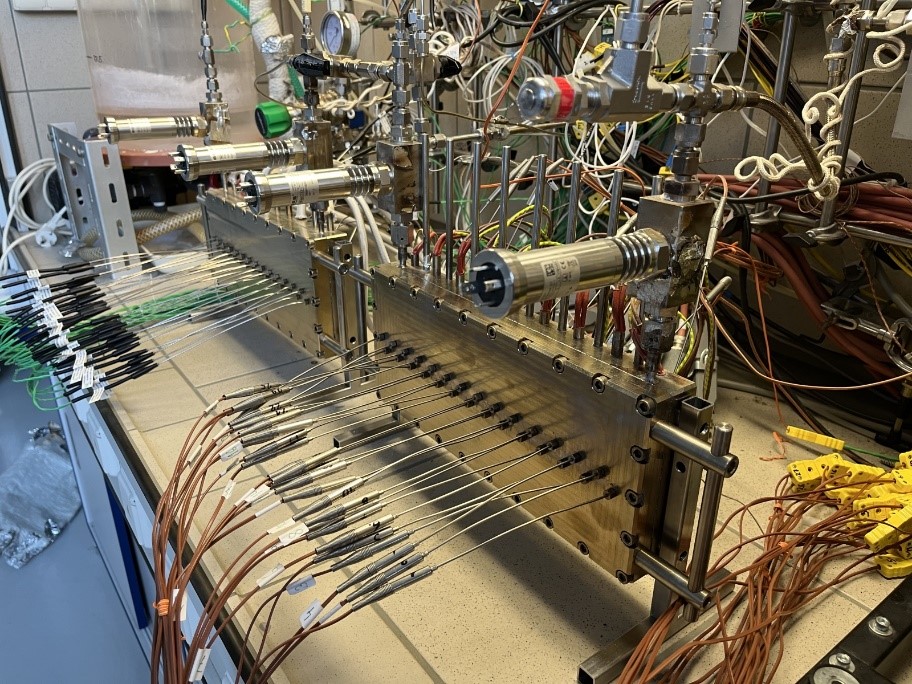 The beneficial features of micro- and mili-reactors such as high surface-to-volume ratio and good control of reaction conditions (temperature, pressure) are applied to study the catalytic selective oxidations for the field of specialty chemicals. We have developed, designed, and manufactured a catalytic reactor with a long reaction path that allows us to study the oxidation process on the catalyst under industrially relevant conditions (catalyst shape, temperature, pressure, and flow conditions).
The beneficial features of micro- and mili-reactors such as high surface-to-volume ratio and good control of reaction conditions (temperature, pressure) are applied to study the catalytic selective oxidations for the field of specialty chemicals. We have developed, designed, and manufactured a catalytic reactor with a long reaction path that allows us to study the oxidation process on the catalyst under industrially relevant conditions (catalyst shape, temperature, pressure, and flow conditions).
Apparatus with two milli-reactors for studying selective oxidations in the gas phase under conditions corresponding to an industrial reactor
Other results
- Stavárek P., Jaklová N., Večeř M., Zelenka L., Bernat S., Armada S., Alnes Ø.: The Current State of Environmentally Acceptable Lubricants in Stern Tube Lubrication: A Review. J. Tribol. 147(10), 100801, 2025. DOI
- Zažímal F., Plasienka D., Atri S., Vrána L., Monfort O., Stavárek P., Klusoň P., Sob M., Homola T.: Unveiling the effect of the polymerization degree of graphitic carbon nitride on the surface functionalization by low-temperature plasma: Insights from XPS and DFT study. Appl. Surf. Sci. 699(1 Aug), 163073, 2025. DOI
- Reháčková M., Veith M., Stavárek P., Zedniková M., Orvalho S., Pěnkavová V., Jaklová N., Maliková S., Klusoň P.: Chemical Engineering View on the Silicone Oil Utilization in the Treatment of Retinal Detachment. ChemBioEng Rev. 11(6), e202400090, 2024. DOI
- Vesely M., Dzik P., Ettler K., Wertzova V., Kubac L., Kluson P.: Disposable indicator card for personal monitoring of solar exposure, J. Photochem. Photobiol. A-Chem. 454(1 Sep) 115741, 2024. DOI
- Večeř M., Stavárek P., Krčková S., Zelenka L., Armada S.: Environmentally Acceptable Lubricants for Stern Tube Application: Shear Stability and Friction Factor. Lubricants 12(9), 323, 2024. DOI
- Bernat S., Di Bartolomeo F., Armada S., Valaker E., Bonturi N., Koseto D., Haugen T., Kvernbråten A.K., Stavárek P., Vecer M., Zelenka L.: Exploring the potential of microbial biomass and microbial extracted oils in tribology: a sustainable frontier for environmentally acceptable lubricants. Green Chem. Lett. Rev. 17(1), 2330644, 2024. DOI
- Bourassi M., Lafaye G., Gombert B., Klusoň P., Barbier J.: Catalytic wet air oxidation of sulfamethoxazole and tetracycline using platinum-based catalysts at eco-operating conditions. J. Clean. Prod. 429(1 Dec), 139453, 2023. DOI
- Dolai S., Bhunia S.K., Kluson P., Stavarek P., Pittermannova A., Solvent-Assisted Synthesis of Supramolecular-Assembled Graphitic Carbon Nitride for Visible Light Induced Hydrogen Evolution – A Review, ChemCatChem 14(4), e202101299, 2022. DOI